TD1 - Bilan de liaison
1 - Introduction
| Limiting link | - | UL |
|---|
| UL ratio | pUL | 0.2 |
| Target cell edge data rate [Mbps] | D | 20.0 |
| Carrier frequency [GHz] | fc | 28 |
| Allocated bandwidth [MHz] | W | 100 |
| BS antenna height [m] | hb | 33 |
| UE antenna height [m] | hm | 1.50 |
| Coverage probability | pc | 0.90 |
| NLOS propagation | - | YES |
| Indoor coverage | - | NO |
| Shadowing standard deviation [dB] | σ | 6 |
| Number of HARQ retransmissions | Nh | 4 |
2 - Transmission
1. Compute the EIRP and the transmit diversity gain
On a Ptx=23dBm et Na=2
EIRP=Ptx+Gtx−L
Transmit diversity gain :
Gtx=10log10(Ntx)
On calcule :
EIRP=23+10log2−0EIRP=23+3.01EIRP=26.01dBm
3 - Reception
2. Compute the target SINR.
SNR=10log10(β(2αWCcible−1))
On utilise pUL et D de l'énoncé
Ccible=pULD=0.220=100Mbps
On connait α=1 et β=1 et W=100MHz
SNR=10log10(1(21⋅100100−1))SNR=10log10(2100100−1)SNR=10log10(21−1)SNR=10log10(2−1)SNR=10log10(1)SNR=10⋅0SNR=0
D'après l'énoncé, on a Li=3dB
SINRcible=SNR+LiSINRcible=0+3SINRcible=3dB
3. Compute the noise power at the receiver.
On a
- N0=−174dBm/Hz
- W=100MHz
- NF=3dB
En W
��N=N0⋅W⋅NF
En dBm :
N=−174+10⋅log(W)+NFN=−174+10⋅log(100⋅106)+3N=−174+10⋅8+3N=−174+80+3N=−91dBm
4. Compute the receive array gain, the receive antenna gain and the diversity gain.
On a
- NbAE=128
- NbAP=2
- Gae=8dBi
Garray=10⋅log10(NbAPNbAE)Garray=10⋅log10(2128)Garray=10⋅log10(2128)Garray=10⋅1.80617997398Garray=18.06dB
Gdiversity=10⋅log10(NbAP)Gdiversity=10⋅log10(2)Gdiversity=10⋅0.301Gdiversity=3.01dB
Le gain de l'antenne de réception correspond au gain d'un élément d'antenne Gae=8dBi
5. After including typical scheduling gain and HARQ gain, compute the sensitivity of the receiver.
La valeur typique du gain d'ordonnancement est de Gs=3dB
Dans l'énoncé on a Nh=4
GHARQ=10⋅log10(Nh)GHARQ=10⋅log10(4)GHARQ=6dB
S=SINR+N−GS=SINR+N−Garray−Gdiversity−Gae−Gs−GHARQS=3+(−91)−18.06−3.01−8−3−6S=−126.07dBm
4 - Margins
6. Compute the shadowing margin.
On connait
- d'après l'énoncé σ=6dB
- d'après l'énoncé pc=0.9
- Pout=1−pc=1−0.9=0.1
On utilise la formule de Jakes
Ks=σQ−1(Pout)
On sait que Q−1(0.1)=1.28
Ks=6Q−1(0.1)Ks=6⋅1.28Ks=7.68dB
7. Refer to Raghavan et al., 2019 and propose a hand and body loss for our link budget.
On utilise les valeurs de la table 1 de l'article
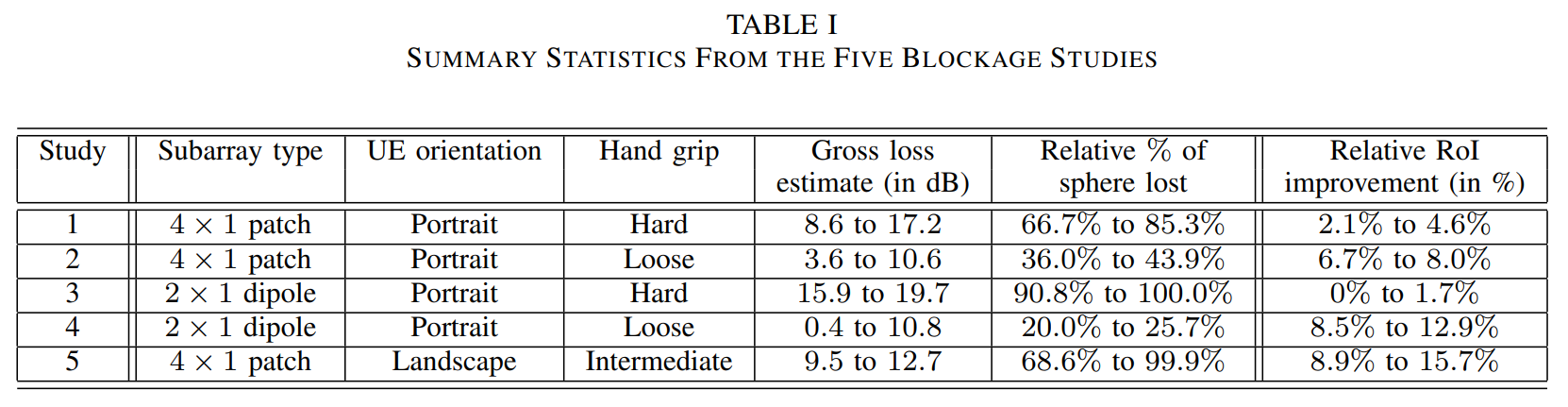
On regarde les lignes Subarray type 2 x 1 dipole. On choisit de prendre le “Hard Hand Grip” car c'est le pire des cas
On a donc Khl=15dB
8. Compute the indoor penetration loss when indoor coverage is required up to 1m.
On regarde le modele 3GPP 38901-g10-channel-models.pdf et on utilise le O2I building penetration loss.
On a fc=28
PL=PLb+PLtw+PLin+N(0,σP2)
PLin=0.5⋅d=0.5dB
On utilise le modèle de low-loose model pour PLtw (d'après l'article):
PLtw=5−10log10(pglass⋅1010−Lglass+pconcrete⋅1010−Lconcrete)PLtw=5−10log10(0.3⋅1010−(2+0.2∗fc)+0.7⋅1010−(5+4∗fc))PLtw=5−10log10(0.3⋅1010−(2+0.2∗28)+0.7⋅1010−(5+4∗28))PLtw=5−10log10(0.3⋅10103.6+0.7⋅10105+4∗28)PLtw=5−10log10(0.3⋅100.36+0.7⋅1010117)PLtw=5−10log10(0.3⋅100.36+0.7⋅1011.7)PLtw=17.8dB
On trouve donc PL=0.5+17.8=18.3dB
9. Refer to Bas et al., 2018 and propose a foliage loss for our link budget.
On a dv = 2m$
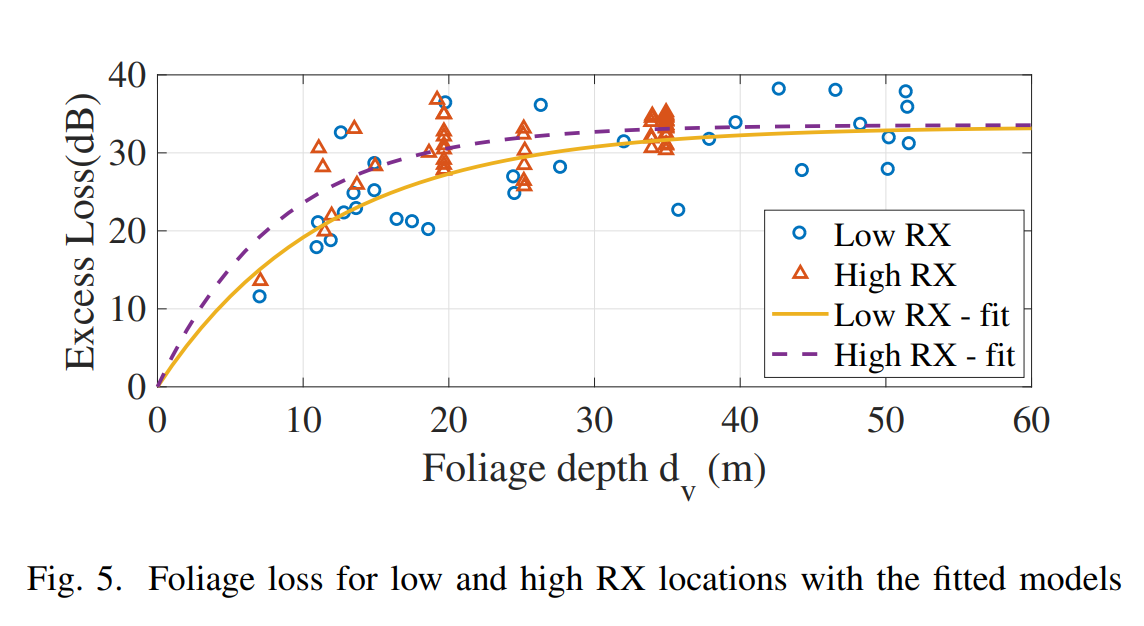
On trouve donc 4.5dB
10. Refer to Azar et al., 2013 and propose a rain loss for our link budget.
On connait fc=28GHz
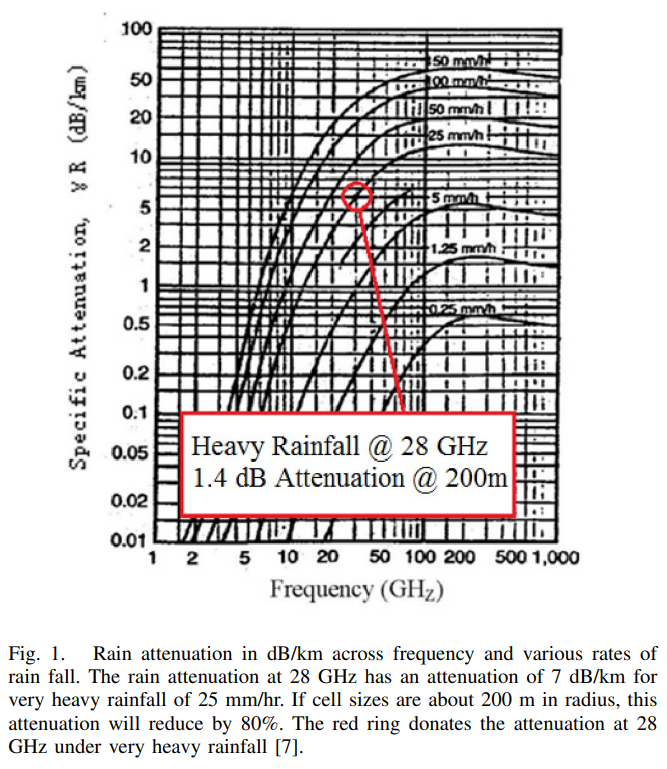
On trouve donc Rainloss=1.4dB
5 - Cell radius
11. Compute the MAPL and the cell range indoor and outdoor.
Modele 3GPP 38901-g10-channel-models.pdf.
On connait
- PIRE=26.01dBm
- S=−126.07dBm
- Mi=0.5dB
- Ks=7.68dB - shadowing margin
- Garray=18.06dB
- Gdiversity=3.01dB
- Gae=8dBi
- Khl=15dB - hand and body loss
- Floss=4.5dB
- Rainloss=1.4dB
- PL=18.3dB - indoor penetration loss
Cas "cell range indoor" :
MAPL=PIRE−S−Marges−Pertes+GainMAPL=26.01−(−126.07)−Mi−Ks�−Khl−PL−Floss−Rainloss+MAPL=26.01−(−126.07)−0.5−7.68−15−18.3−4.5−1.4MAPL=104.7dB
Cas "cell range outdoor" :
MAPL=PIRE−S−Marges−Gains−PertesMAPL=26.01−(−126.07)−Mi−Ks−Khl−Floss−RainlossMAPL=26.01−(−126.07)−0.5−7.68−15−4.5−1.4MAPL=123dB
On utilise la formule de NLOS propagation :
PLUMA−NLOS=13.54+39.08log10(d3D)+20log10(fc)−0.6(hUT−1.5)
On inverse la formule pour avoir donc :
d3D=1039.08PLUMA−NLOS−13.54−20log10(28)+0.6(hUT−1.5)
On connait aussi :
- hBS=33m
- hUT=1.5m
- fc=28GHz
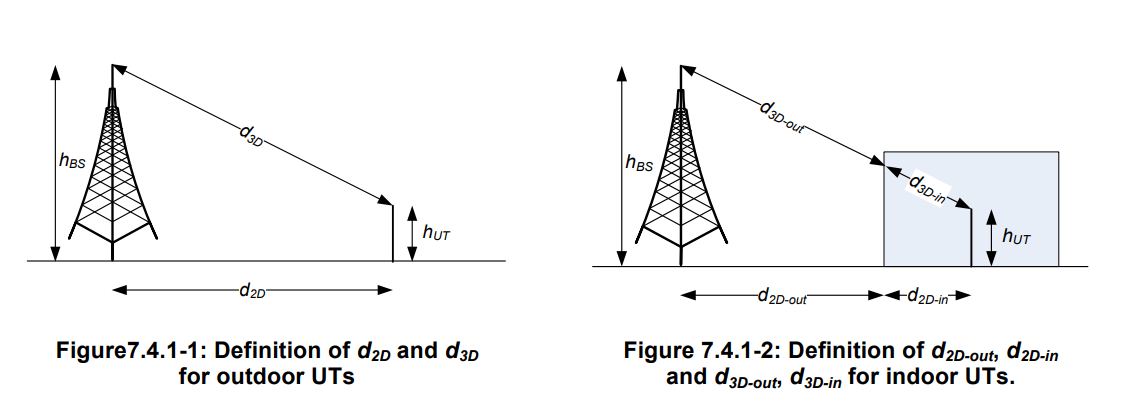
Or nous voulons pour d2D
d2D=(d3D)2−(hBS−hUT)2
On trouve donc d3D−in=39.09m et d2D−in=23.14m
On trouve donc d3D−out=114.9m et d2D−out=110.5m
6 - Deployment scenario in Paris 13
12. Deployment scenario in Paris 13
On connait :
- la formule de l'aire d'un cercle : S=π⋅R2 donc la formule du rayon d'un cercle : πS
- la surface de Paris 13 : 7.15km2
- le nombre de sites LTE : 31
Surface moyenne d'une cellule :
Smoy=NbLTEAireParis13Smoy=317.15Smoy=0.230km2
Le rayon moyen d'une cellule :
Rmoy=πSmoyRmoy=π0.230Rmoy=0.073Rmoy=0.27kmRmoy=270m
13. What is the proportion of Paris 13 area that could be covered with mmW if only LTE sites were reused?
Airemoy=NbLTE⋅π⋅d2D−out2Airemoy=31⋅π⋅(110.5∗10−3)2Airemoy=1.18km2
Proportion=AireParis13AiremoyProportion=7.150.46Proportion=16%
14. How many mmW sites would be needed to cover the whole area?
Nbsite=AirecellAireParis13Nbsite=π⋅d2D−out2AireParis13Nbsite=π⋅(110.5∗10−3)27.15Nbsite=186
15. Same questions if the target cell edge data rate is set to 5 Mbps.
Ccible=0.25=25MbpsSNR=10log10(21⋅10025−1)=−7.23dBSINR=−7.23+3=−4.23dBS=−133.3dBmMAPLout=130.23dBd3D−out=173.6md2D−out=170.7mNbsite=7.15/(π⋅(170.7∗10−3)2)=78
16. Same questions if the target cell edge data rate is set to 5 Mbps and indoor coverage is required.
Ccible=0.25=25MbpsSNR=10log10(21⋅10025−1)=−7.23dBSINR=−7.23+3=−4.23dBS=−133.3dBmMAPLindoor=111.93dBd3D−out=59.85md2D−out=50.9mNbsite=7.15/(π⋅(170.7∗10−3)2)=878


